THE EDUCATION SYSTEM / STRUCTURE
The education system in United states of America offers a vast range of choices for international students. A student can choose from many institutions, programs and locations in USA.
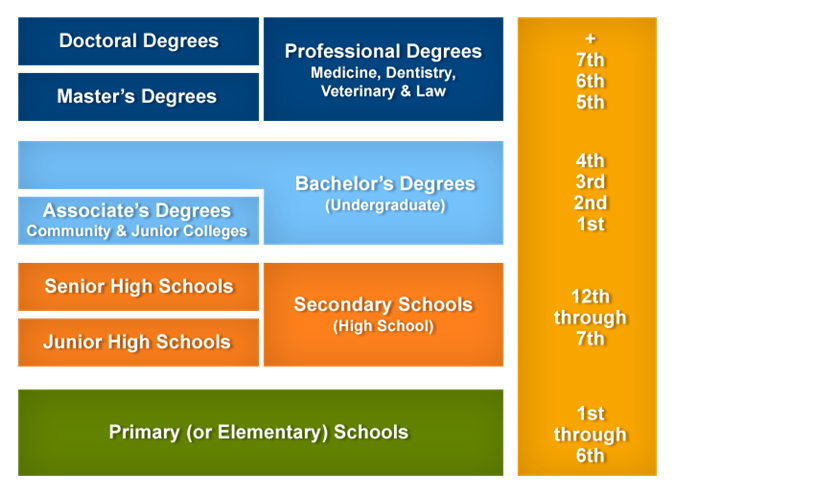
A student attends primary and Secondary education for 12 years before getting eligible for Higher education. Upon successful completion of 12 years a student gets a certificate or Diploma of High School which is equivalent to grade 12.
A student who is attending a college or university and has not earned a bachelor’s degree, is studying at the undergraduate level. It typically takes about four years to earn a bachelor’s degree. One can earn his Bachelor’s degree at a College or community college at university.
A first year student is called “Freshman” and second year “Sophomore”. When a Student enters into third year he is known as “Junior” and Final year students are usually called “Seniors”.
A student can choose his Major in one area focusing on one particular field/subject and can do a Minor degree in another area. A “major” is the specific field of study in which your degree is focused.
Many students choose to study at a community college in order to complete the first two years of prerequisite courses. They will earn an Associate of Arts (AA) transfer degree and then transfer to a four-year university or college. You must choose your major at the beginning of your third year of school.
Master level programs are available in various streams. One generally requires a Bachelors degree to get admission into a Graduate Program. It takes usually 2 years to complete Masters degree in USA.
A graduate program is usually a division of a university or college. To gain admission, you will need to take the GRE (graduate record examination). Certain master’s programs require specific tests, such as the LSAT for law school, the GRE or GMAT for business school, and the MCAT for medical school.
Graduate programs in pursuit of a master’s degree typically take one to two years to complete. For example, the MBA (master of business administration) is an extremely popular degree program that takes about two years. Other master’s programs, such as journalism, only take one year.
The majority of a master’s program is spent in classroom study and a graduate student must prepare a long research paper called a “master’s thesis” or complete a “master’s project.”
Many graduate schools consider the attainment of a master’s degree the first step towards earning a PhD (doctorate). But at other schools, students may prepare directly for a doctorate without also earning a master’s degree. It may take three years or more to earn a PhD degree. For international students, it may take as long as five or six years.
For the first two years of the program most doctoral candidates enroll in classes and seminars. At least another year is spent conducting firsthand research and writing a thesis or dissertation. This paper must contain views, designs, or research that have not been previously published.
A doctoral dissertation is a discussion and summary of the current scholarship on a given topic. Most U.S. universities awarding doctorates also require their candidates to have a reading knowledge of two foreign languages, to spend a required length of time “in residence,” to pass a qualifying examination that officially admits candidates to the PhD program, and to pass an oral examination on the same topic as the dissertation.
Community colleges are two-year colleges that award an Associate’s degrees (transferable), as well as certifications. There are many types of associate degrees, but the most important distinguishing factor is whether or not the degree is transferable. Usually, there will be two primary degree tracks: one for academic transfer and the other prepares students to enter the workforce straightaway. University transfer degrees are generally associate of arts or associate of science. Not likely to be transferrable are the associate of applied science degrees and certificates of completion.
Community college graduates most commonly transfer to four-year colleges or universities to complete their degree. Because they can transfer the credits they earned while attending community college, they can complete their bachelor’s degree program in two or more additional years. Many also offer ESL or intensive English language programs, which will prepare students for university-level courses.
A state school is supported and run by a state or local government. Each of the 50 U.S. states operates at least one state university and possibly several state colleges. Many of these public universities schools have the name of the state, or the actual word “State” in their names: for example, New York State University or University of Michigan.
These schools are privately run as opposed to being run by a branch of the government. Tuition will usually be higher than state schools. Often, private U.S. universities and colleges are smaller in size than state schools.
Religiously affiliated universities and colleges are private schools. Nearly all these schools welcome students of all religions and beliefs. Yet, there are a percentage of schools that prefer to admit students who hold similar religious beliefs as those in which the school was founded.
An institute of technology is a school that provides at least four years of study in science and technology. Some have graduate programs, while others offer short-term courses.
The school calendar usually begins in August or September and continues through May or June. The majority of new students begin in autumn, so it is a good idea for international students to also begin their U.S. university studies at this time. There is a lot of excitement at the beginning of the school year and students form many great friendships during this time, as they are all adjusting to a new phase of academic life. Additionally, many courses are designed for students to take them in sequence, starting in autumn and continuing through the year.
The academic year at many schools is composed of two terms called “semesters.” (Some schools use a three-term calendar known as the “trimester” system.) Still, others further divide the year into the quarter system of four terms, including an optional summer session. Basically, if you exclude the summer session, the academic year is either comprised of two semesters or three quarter terms.
